
Course Content
Formula Sheet
Example 1
A trolley is positioned 2·0m from a light gate which is connected to a timer as shown.
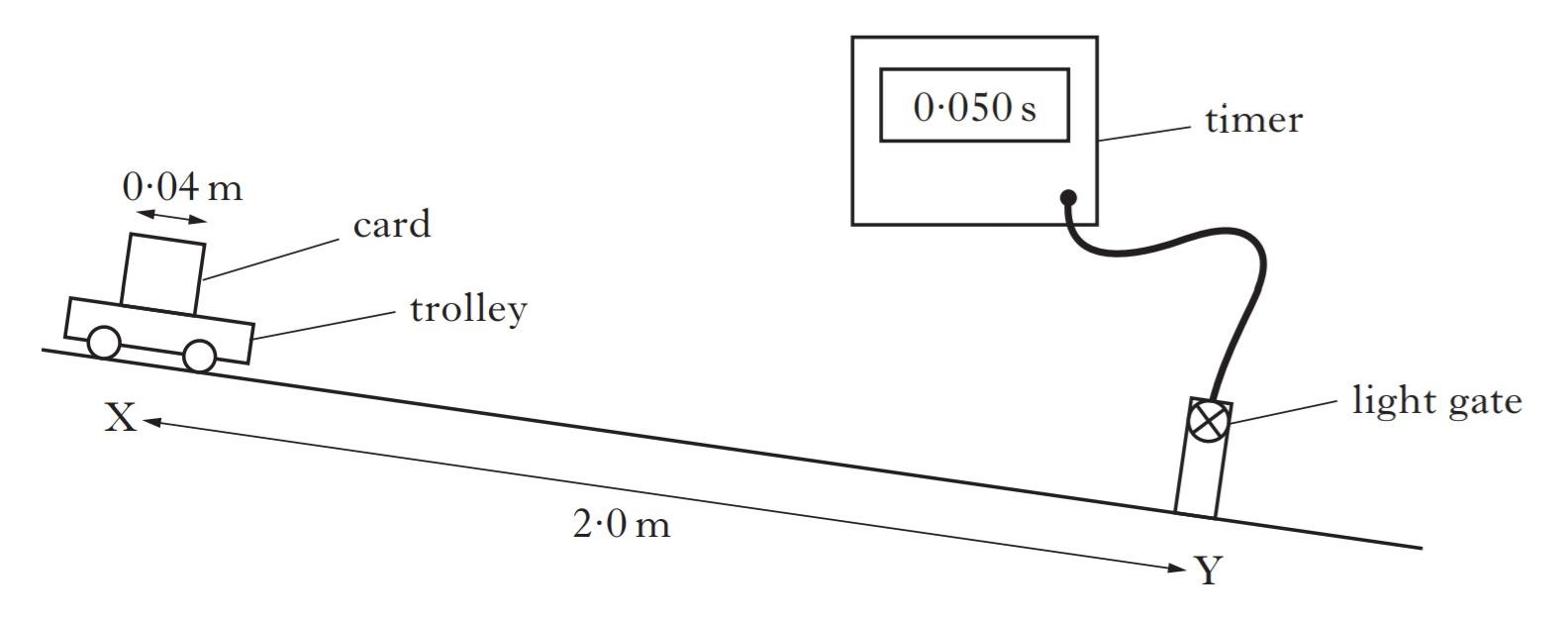
The trolley is released from rest and takes 5·0s to reach the light gate.
The time taken for the card on the trolley to pass through the light gate is 0·050s.
What is the average speed of the trolley between X and Y?
In this question, we are given a lot of information.
It is important that we acknowledge what the question is actually asking.
We are asked for the average speed between X and Y.
With this in mind, we can use:
v = d⁄t
v = 2⁄5
v = 0.4ms-1
Example 2
A stone is projected horizontally from a cliff.

The initial speed of the stone is 20ms-1
The stone hits the ground at X, 3·0s after being projected.
The effect of air resistance can be ignored.
What is the horizonal speed and the vertical speed of the stone just before it hits the ground at X?
You should know that the horizontal speed of the stone does not change; it is equal to the inital speed of 20ms-1.
To work out the vertical speed of the stone, we need to list our data:
initial vertical speed(u) = 0ms-1
acceleration(a) = 9.8ms-2
final vertical speed(v) = ?
Now, we can use:
a = v - u⁄t
v = at
v = 9.8 x 3
v = 29.4ms-1
So
horizonal speed = 20ms-1
vertical speed = 29.4ms-1
Example 3
A diagram of a slide is shown below.
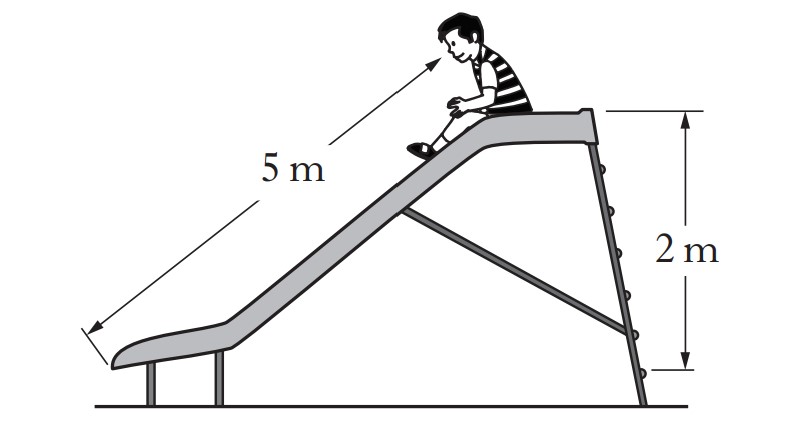
A child of weight 250N slides from the top to the bottom.
What is the change in gravitational potential energy of the child?
First, lets identify the formula we need to use.
We are asked for the change in gravitational potential energy, which is effectively how much energy is lost.
So we can use:
Ep = mgh
Notice how we don't actually have the mass of the child, so we need to work this out using:
w = mg
Now we sub in our values and re-arrange:
250 = m x 9.8
m = 250⁄9.8
m = 25.5kg
Now we can calculate the change in gravitational potential energy:
Note that the height whenever dealing with gravitational potential energy is the vertical height:
Ep = 25.5 x 9.8 x 2
Ep = 499.8
Ep = 500J
Example 4
The diagram shows the horizontal forces acting on a box.
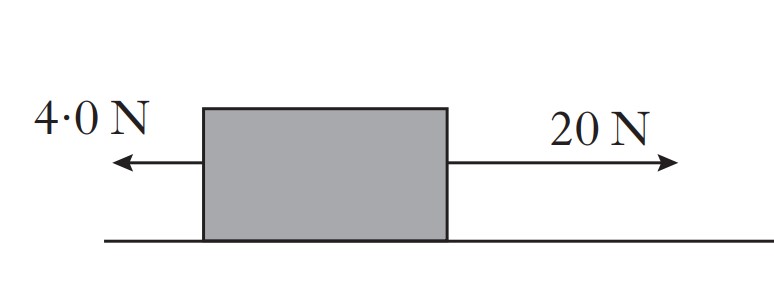
The box accelerates at 1.6ms-2
What is the mass of the box?
First, lets calculate the unbalanced force acting on the box:
Unbalanced Force(FUN) = Total Force - Frictional Force
FUN = 20 - 4
FUN = 16N
Now that we have the unbalanced force(FUN) and the acceleration(a), we can use and re-arrange:
FUN = ma
16 = m x 1.6
m = 16⁄1.6
m = 10kg
Example 5
An aircraft is flying horizontally at a constant speed.
(a) The aircraft and passengers have a total mass of 50 000kg. Calculate the total weight.
(b) State the magnitude of the upward force acting on the aircraft.
(c) During the flight, the aircraft's engines produce of 4.4 x 104N due North.
The aircraft encounters a crosswind, blowing from west to east,
which exerts a force of 3.2 x 104N.
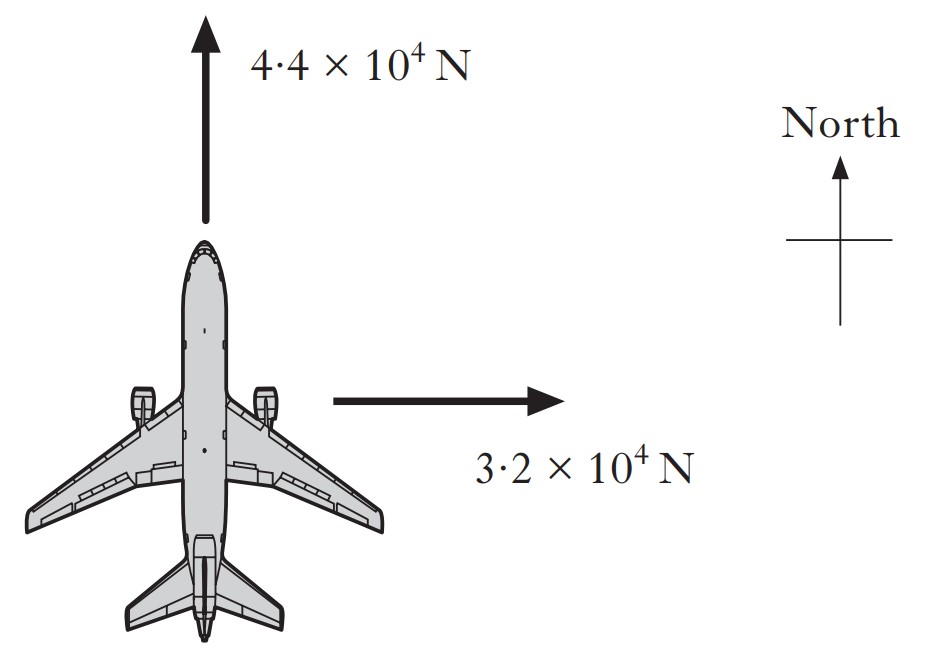
Calculate the resultant force on the aircraft.
(a) A simple question, using:
w = mg
w = 50 000 x 9.8
w = 490 000N
(b) The trick to this question is in the wording, where it says "State".
This usually means no calculations need to be done.
Since the plane is flying horizontally at a constant height:
Upward Force = 490 000N
(c) We always need a diagram for calculating resultant force.
Remember to draw vectors tip to tail:

Where "F" is the magnitude of the resultant force, and "x" is the direction of the resultant force.
Now we use pythagoras to calculate the magnitude of the resultant force:
F 2 = (3.2 x 104)2 + (4.4 x 104)2
F = 5.4 x 104N
Now we calculate the direction of the resultant force:
tan x = opp⁄adj
tan x = 3.2 x 104⁄4.4 x 104
x = tan-1( 3.2 x 104⁄4.4 x 104 )
x = 54°
We need the direction as a bearing, so we draw a North line on our diagram.
Then we subtract the angle we just calculated from 90 to get the bearing:
So the bearing is 036(Remember bearings are displayed with only three figures)
Finally, we need to state the resultant force:
Resultant Force = 5.4 x 104N at a bearing of 036
Example 6
A balloon of mass 400kg rises vertically from the ground.

The graph shows how the vertical speed of the ballon changes during the first 100s of its upward flight.
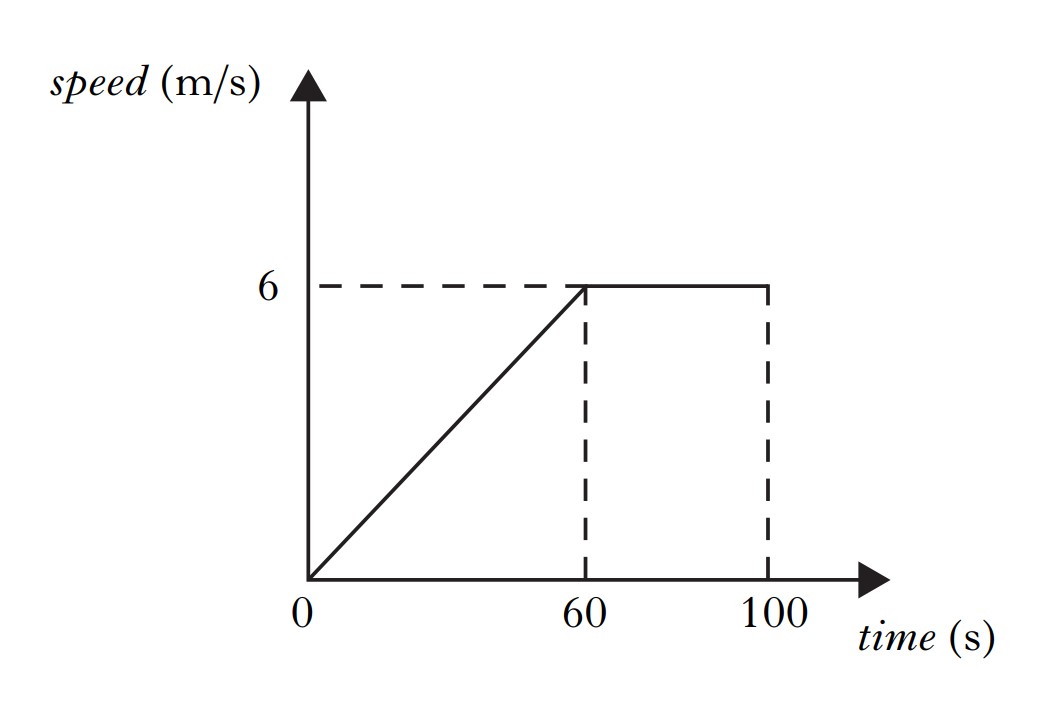
(a) Calculate the acceleration of the balloon during the first 60s.
(b) Calculate the distance travelled by the balloon in 100s.
(c) Calculate the average speed of the balloon during the first 100s.
(d) Calculate the weight of the balloon.
(e) Calculate the total upward force acting on the balloon during the first 60s of its flight.
(a) To get the acceleration, we use:
a = v - u⁄t
Where v is the final vertical speed, u is the inital vertical velocity and t is the time.
Subbing in our values:
a = 6 - 0⁄60
a = 0.1ms-2
(b) To get the distance travelled, we need to calculate the area under the graph.
We need to split the graph into two separate areas:
d = area under speed time graph:
d = (0.5 x 60 x 6) + (40 x 6)
d = 420m
(c) Simply just use the speed formula:
v = d⁄t
a = 420⁄100
v = 4.2ms-1
(d) Simply just use the weight formula:
w = mg
w = 400 x 9.8
w = 3920N
(e) The best way to go about this question is to draw a freebody diagram to get a sense of what is actually happening:
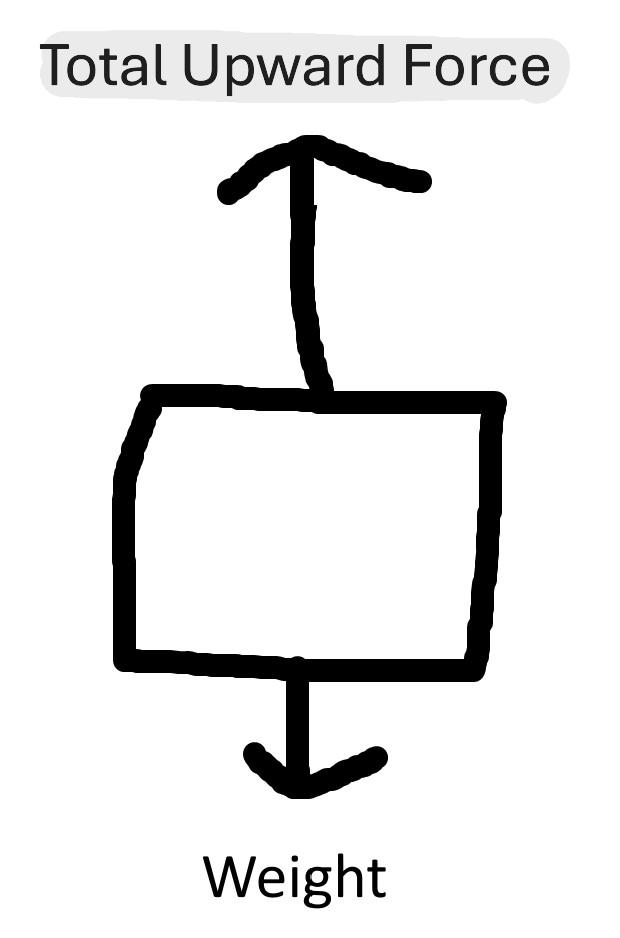
For the balloon to accelerate upwards, the total upward force must be greater than the size of the weight of the balloon.
This means that there will be an unbalanced force acting upwards, causing an the balloon to accelerate upwards.
To calculate the size of the unbalanced force, we use:
FUN = ma
FUN = 400 x 0.1
FUN = 40N
Now, we add the unbalanced force to the weight to get the total upward force.
Total upward force = FUN + Weight
Total upward force = 40 + 3920
Total upward force = 3960N